阅读完需:约 9 分钟
一、ServletContext介绍
javaee标准规定了,servlet容器需要在应用项目启动时,给应用项目初始化一个ServletContext作为公共环境容器存放公共信息,ServletContext中的信息都是由容器提供的。
在web项目中,web.xml文件我们通常有如下配置:
<context-param>
<param-name>key</param-name>
<param-value>value123</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>com.brolanda.contextlistener.listener.ContextListenerTest</listener-class>
</listener> ServletContextListener的实现类代码如下(即上面的listener实现类):
public class ContextListenerTest implements ServletContextListener {
//容器启动时执行该方法
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
String value = servletContext.getInitParameter("key");
System.out.println(" ContextListenerTest contextInitialized , key value is " + value + " .......");
}
//容器结束时执行该方法
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
System.out.println(" ContextListenerTest contextDestroyed ......");
}
}此时启动Web容器,执行流程如下:
1、启动一个WEB项目的时候,容器(如:Tomcat)会去读它的配置文件web.xml,读两个节点: <listener></listener> 和 <context-param></context-param>;
2、紧接着,容器创建一个ServletContext(上下文),在该应用内全局共享;
3、容器将<context-param></context-param>转化为键值对,并交给ServletContext;
4、容器创建中的类实例,即创建监听,该监听器必须实现自ServletContextListener接口,如Log4jConfigListener,或者如上自定义实现类(如果不自定义实现,可以使用实现类ContextLoaderListener)
5、Web项目启动中,在监听类中ontextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)初始化方法会被执行,在该方法中获取到ServletContext和全局参数;
6、得到这个context-param的值之后,你就可以做一些操作了。这个时候你的WEB项目还没有完全启动完成,这个动作会比所有的Servlet都要早。换句话说,这个时候,你对<context-param>中的键值做的操作,将在你的WEB项目完全启动之前被执行。
7、Web项目结束时,监听类中的contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event)方法会被执行;
简单来说流程就是:1、读配置文件节点–>2、创建ServletContext–>3、设置参数到Context中–>4、监听listener并执行初始化方法和销毁方法。
二、Spring Web应用上下文配置
Spring分别提供了用户启动WebApplicationContext的Servlet和Web容器监听器:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderServlet
所有版本的WEB容器都可以定义自启动的Servlet,但只有2.3及以上的版本的WEB容器才支持Web容器监听器,现在一般都使用Listener了。
Spring3.0以后就找不到ContextLoaderServlet这个类了,Spring3.0以后移除ContextLoaderServlet,使用ContextLoaderListener,
ContextLoaderListener 与 ContextLoaderServlet本质上是等同的,都是调用ContextLoader来加载web程序的上下文。
加载完成以后,都是在ServletContext中,只不过listener需要Servlet2.3及以上支持。
-
ContextLoaderListener是在我们的web容器启动的时候启动的,默认会加载/WEB-INF/下面的applicationContext.xml文件。并创建一个RootWebApplicationContext容器。 -
DispatcherServlet是在我们第一次访问我们的应用的时候创建的。这时候它默认会将配置在/WEB-INF下面的-servlet.xml配置文件,然后也创建一个WebApplicationContext。这个WebApplicationContext将之前ContextLoaderListener创建的容器作为父容器,(ContextLoaderListener创建的也是一个WebApplicationContext是RootWebApplicationContext)因此在父容器中配置的所有Bean都能够被注入到子容器中。
Spring为我们提供的IOC容器,需要我们指定容器的配置文件,然后由该监听器初始化并创建该容器。指定配置文件的地址及文件名称,一定要使用:contextConfigLocation作为参数名称。如下:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml,/WEB-INF/jason-servlet.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>该监听器,默认读取/WEB-INF/下的applicationContext.xml文件。但是通过context-param指定配置文件路径后,便会去你指定的路径下读取对应的配置文件,并进行初始化。项目启动时,便会执行类ContextLoaderListener的相关方法,创建Root WebApplicationContext(Web应用上下文)并以键值对形式存放与ServletContext中。
在web.xml中,可以配置多个Servlet,如下:
<servlet>
<init-param>
<param-name>param1</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:ServletDemo-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>demo.ServletDemo</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>SpringIOC容器先根据监听初始化Root WebApplicationContext,然后再初始化web.xml中其他配置的Servlet,为其初始化自己的上下文信息ServletContext,并加载其设置的配置信息和参数信息到该上下文中,将Root WebApplicationContext设置为它的父容器。所以最后的关系是ServletContext包含了Root WebApplicationContext,Root WebApplicationContext包含了其他的Servlet上下文环境。
如下图:
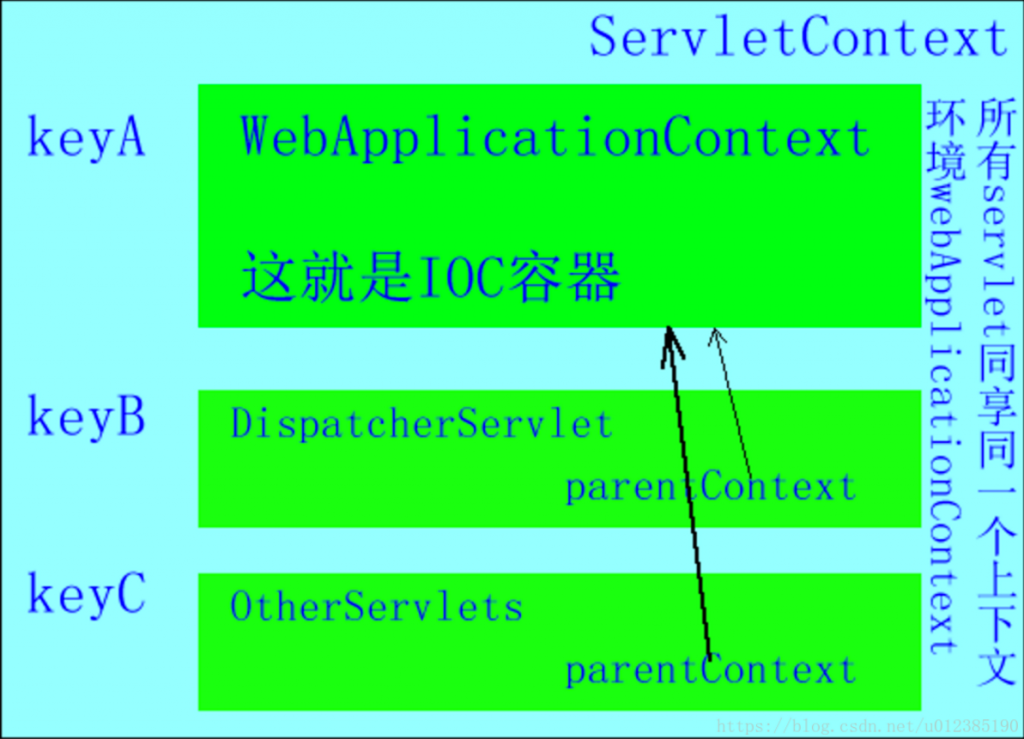
每一个DispatcherServlet定义一个Spring的WebApplicationContext,并且都与一个ContextLoaderListener的Root WebApplicationContext相关
ContextLoaderListener是Spring框架对Servlet监听器的一个封装,本质上还是一个Servlet监听器,它创建了一个根应用程序上下文(ApplicationContext),并与所有DispatcherServlet上下文创建的子上下文共享。
ContextLoaderListener 包含全局可见的bean 的上下文,如服务,存储库,基础结构bean等。创建根应用程序上下文后,它将 ServletContext 作为属性存储,名称为:
// org/springframework/web/context/ContextLoader.java
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
//Where attibute is defined in /org/springframework/web/context/WebApplicationContext.java as
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
要在Spring控制器中获取根应用程序上下文,可以使用 WebApplicationContextUtils 类。
// Controller.java
@Autowired
ServletContext context;
ApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(context);
if(ac == null){
return "root application context is null";
} 如果没有配置Listener参数,只配置了DispatcherServlet时,tomcat启动时是不会初始化Spring Web上下文的,因为Spring Web是基于Spring的,你没有配置Spring,所以也不会启动它的子上下文Spring Web。
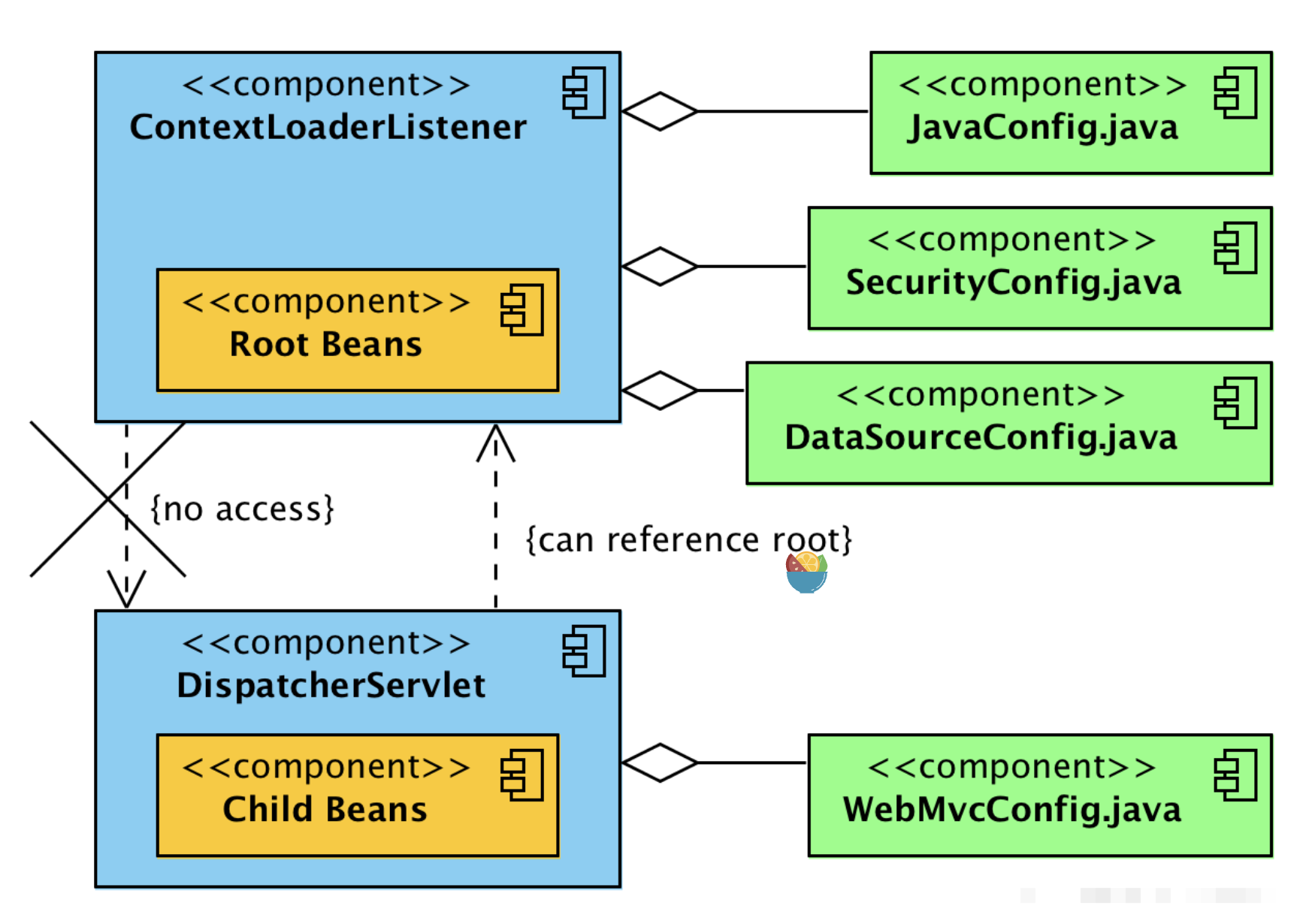
对于作用范围而言,在DispatcherServlet中可以引用由ContextLoaderListener所创建的Root WebApplicationContext中的内容,而反过来不行。
当Spring在执行ApplicationContext的getBean时,如果在自己context中找不到对应的bean,则会在父ApplicationContext中去找。这也解释了为什么我们可以在DispatcherServlet中获取到由ContextLoaderListener对应的Root WebApplicationContext中的bean。
-
ContextLoaderListener创建根应用程序上下文 -
DispatcherServlet条目为每个Servlet条目创建一个子应用程序上下文。 - 子上下文可以访问根上下文中定义的bean。
- 根上下文中的Bean无法直接访问子上下文中的bean。
- 所有上下文都被添加到
ServletContext。 - 你可以使用
WebApplicationContextUtils类访问根上下文。
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
* 初始化根 Web 应用程序上下文。
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
* 关闭根 Web 应用程序上下文。
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
WebApplicationContext
org.springframework.web.context#WebApplicationContext
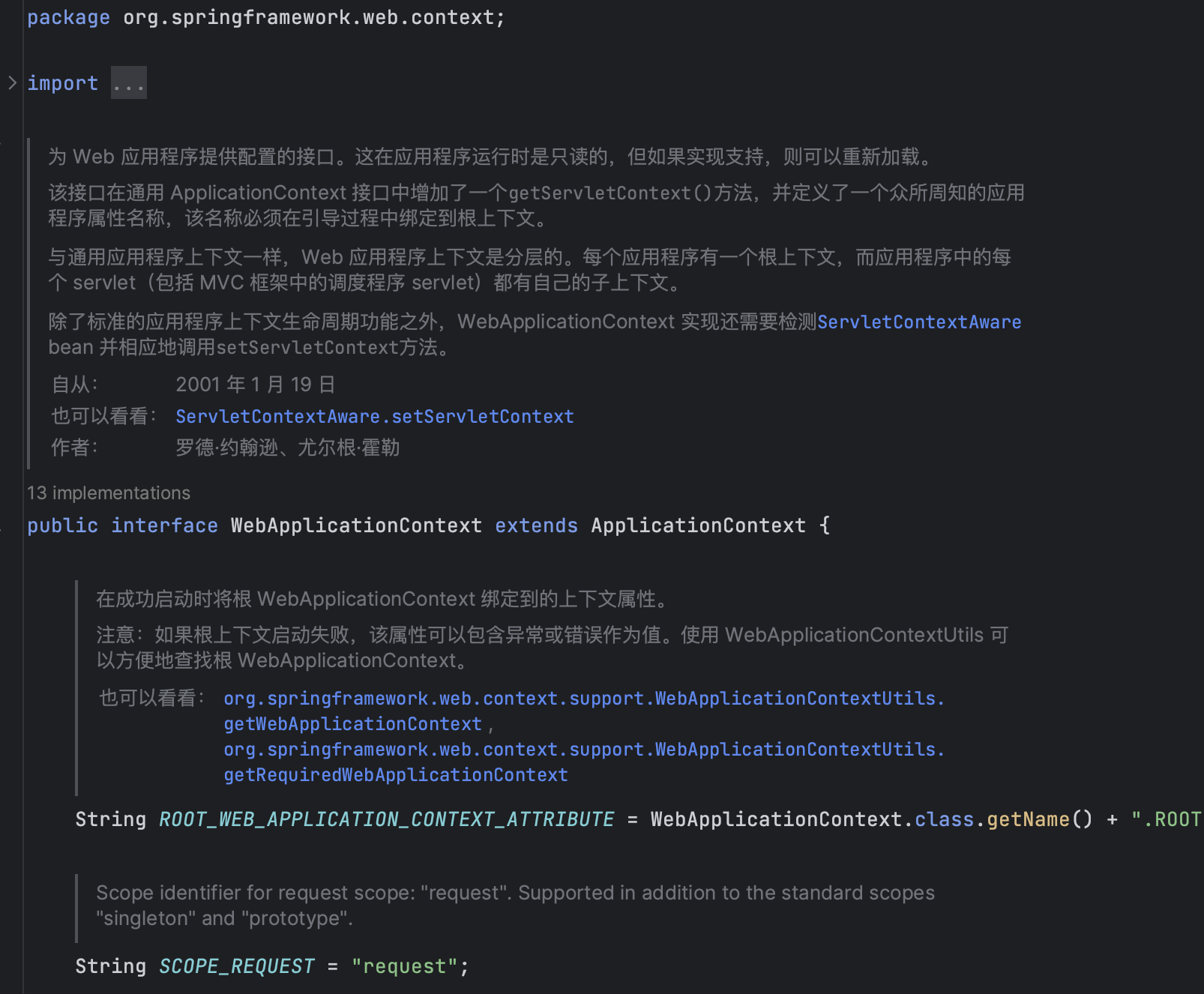
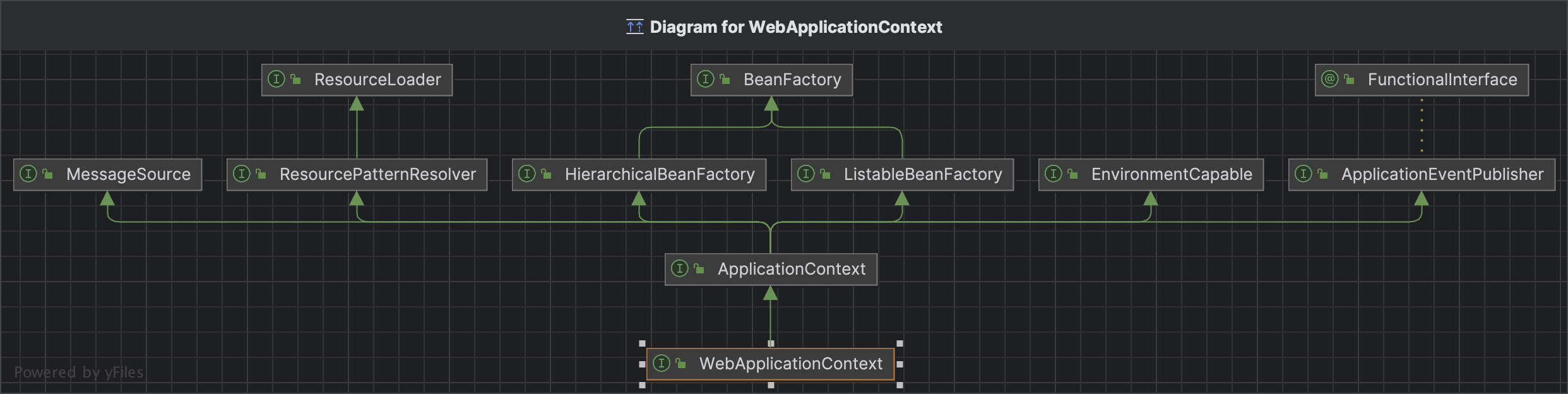
可以通过这个接口来获取ServletContext上下文
// 返回此应用程序的标准 Servlet API ServletContext。
@Nullable
ServletContext getServletContext();如果将ServletContext放入这里的呢,答案就在上面的ContextLoaderListener里
WebApplicationInitializer
在Servlet3.0以后我们可以不需要写xml来配置MVC的参数了,可以通过接口来实现
org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer
或者用AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer抽象类来实现
总结
1、Servlet容器需要在应用项目启动时,给应用项目初始化一个ServletContext作为公共环境容器存放公共信息。
2、WebApplicationContext,是继承于ApplicationContext的一个接口,扩展了ApplicationContext,是专门为Web应用准备的,它允许从相对于Web根目录的路径中装载配置文件完成初始化。
3、在非web应用下,Bean只有singleton和prototype两种作用域,WebApplicaitonContext为Bean添加了三个新的作用域:request/session/global session。
4、Spring分别提供了用户启动WebApplicationContext的Servlet和Web容器监听器(ContextLoaderServlet/ContextLoaderListener);
5、WebApplicationContext实现类:
5-1、XmlWebApplicationContext
采用xml配置,则Spring将使用XmlWebApplicationContext启动Spring容器,即通过XML文件为Spring容器提供Bean的配置信息;
5-2、AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
如果使用@Configure的java类提供配置信息,则需要在xml中进行相关配置,设置contextClass参数值为AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext类,contextConfigLocation参数值则为使用了@Configure注解的类。ContextLoaderListener如果发现配置了contextClass参数,就是使用参数所指定的实现类初始化容器。ApplicationContext接口也有对应的实现类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。