阅读完需:约 10 分钟
Spring Security 这么麻烦,不如自己写一个 Filter 拦截请求,简单实用。
自己写当然也可以实现,但是大部分情况下,大家都不是专业的 Web 安全工程师,所以考虑问题也不过就是认证和授权,这两个问题处理好了,似乎系统就很安全了。
其实不是这样的!
各种各样的 Web 攻击每天都在发生,什么固定会话攻击、csrf 攻击等等,如果不了解这些攻击,那么做出来的系统肯定也不能防御这些攻击。
使用 Spring Security 的好处就是,即使不了解这些攻击,也不用担心这些攻击,因为 Spring Security 已经帮你做好防御工作了。
1.HttpFirewall
在 Spring Security 中提供了一个 HttpFirewall,看名字就知道这是一个请求防火墙,它可以自动处理掉一些非法请求。
HttpFirewall 目前一共有两个实现类:
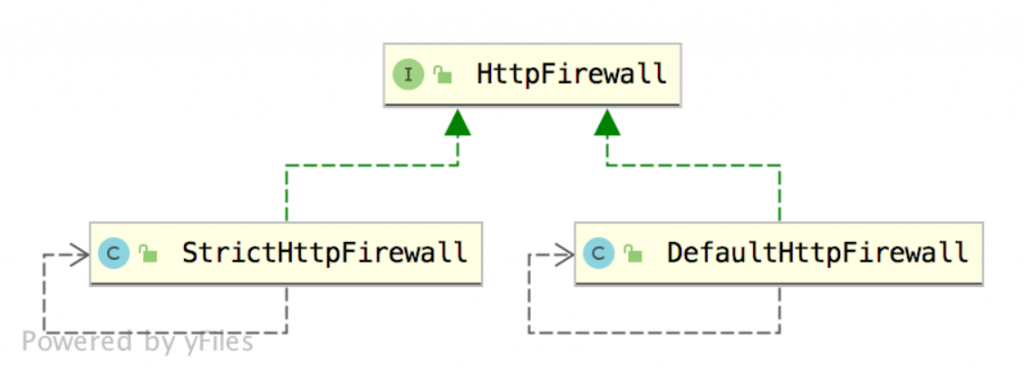
一个是严格模式的防火墙设置,还有一个默认防火墙设置。
DefaultHttpFirewall 的限制相对于 StrictHttpFirewall 要宽松一些,当然也意味着安全性不如 StrictHttpFirewall。
Spring Security 中默认使用的是 StrictHttpFirewall。
2.防护措施
那么 StrictHttpFirewall 都是从哪些方面来保护我们的应用呢?我们来挨个看下。
2.1 只允许白名单中的方法
首先,对于请求的方法,只允许白名单中的方法,也就是说,不是所有的 HTTP 请求方法都可以执行。
这点我们可以从 StrictHttpFirewall 的源码中看出来:
public class StrictHttpFirewall implements HttpFirewall {
private Set<String> allowedHttpMethods = createDefaultAllowedHttpMethods();
private static Set<String> createDefaultAllowedHttpMethods() {
Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
result.add(HttpMethod.DELETE.name());
result.add(HttpMethod.GET.name());
result.add(HttpMethod.HEAD.name());
result.add(HttpMethod.OPTIONS.name());
result.add(HttpMethod.PATCH.name());
result.add(HttpMethod.POST.name());
result.add(HttpMethod.PUT.name());
return result;
}
private void rejectForbiddenHttpMethod(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.allowedHttpMethods == ALLOW_ANY_HTTP_METHOD) {
return;
}
if (!this.allowedHttpMethods.contains(request.getMethod())) {
throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the HTTP method \"" +
request.getMethod() +
"\" was not included within the whitelist " +
this.allowedHttpMethods);
}
}
}从这段代码中我们看出来,你的 HTTP 请求方法必须是 DELETE、GET、HEAD、OPTIONS、PATCH、POST 以及 PUT 中的一个,请求才能发送成功,否则的话,就会抛出 RequestRejectedException 异常。
那如果你想发送其他 HTTP 请求方法,例如 TRACE ,该怎么办呢?我们只需要自己重新提供一个 StrictHttpFirewall 实例即可,如下:
@Bean
HttpFirewall httpFirewall() {
StrictHttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
firewall.setUnsafeAllowAnyHttpMethod(true);
return firewall;
}其中,setUnsafeAllowAnyHttpMethod 方法表示不做 HTTP 请求方法校验,也就是什么方法都可以过。或者也可以通过 setAllowedHttpMethods 方法来重新定义可以通过的方法。
2.2 请求地址不能有分号
不知掉大家有没有试过,如果你使用了 Spring Security,请求地址是不能有 ; 的,如果请求地址有 ; ,就会自动跳转到如下页面:
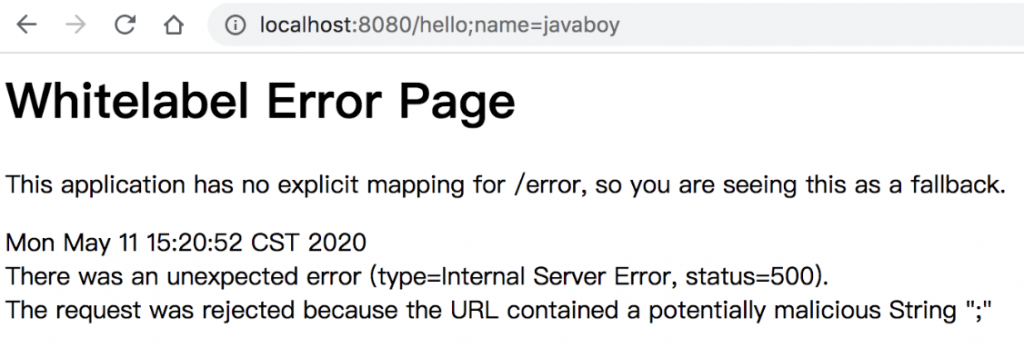
可以看到,页面的提示中已经说了,因为你的请求地址中包含 ;,所以请求失败。
什么时候请求地址中会包含 ; 呢?不知道小伙伴们在使用 Shiro 的时候,有没有注意到,如果你禁用了 Cookie,那么 jsessionid 就会出现在地址栏里,像下面这样:
http://localhost:8080/hello;jsessionid=xx这种传递 jsessionid 的方式实际上是非常不安全的(松哥后面的文章会和大家细聊这个问题),所以在 Spring Security 中,这种传参方式默认就禁用了。
当然,如果你希望地址栏能够被允许出现 ; ,那么可以按照如下方式设置:
@Bean
HttpFirewall httpFirewall() {
StrictHttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
firewall.setAllowSemicolon(true);
return firewall;
}设置完成之后,再去访问相同的接口,可以看到,此时虽然还是报错,但是错误是 404 了,而不是一开始那个不允许 ; 的错了。
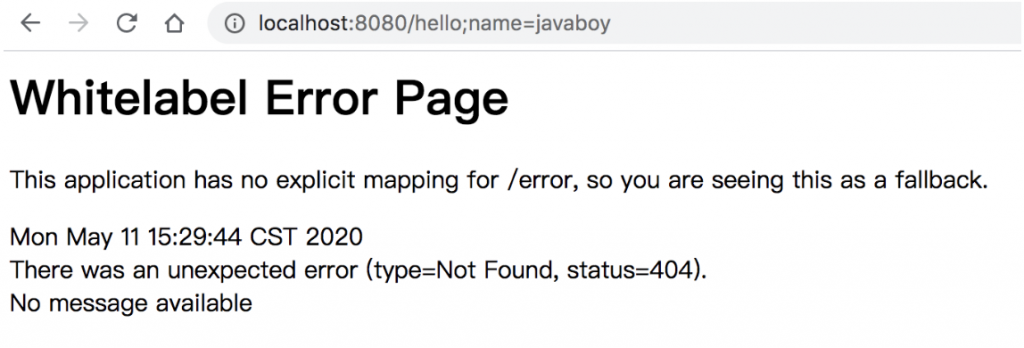
注意,在 URL 地址中,; 编码之后是 %3b 或者 %3B,所以地址中同样不能出现 %3b 或者 %3B
题外话
有的小伙伴可能不知道或者没用过,Spring3.2 开始,带来了一种全新的传参方式 @MatrixVariable。
@MatrixVariable 是 Spring3.2 中带来的功能,这种方式拓展了请求参数的传递格式,使得参数之间可以用 ; 隔开,这种传参方式真是哪壶不开提哪壶。因为 Spring Security 默认就是禁止这种传参方式,所以一般情况下,如果你需要使用 @MatrixVariable 来标记参数,就得在 Spring Security 中额外放行。
接下来我通过一个简单的例子来和大家演示一下 @MatrixVariable 的用法。
我们新建一个 /hello 方法:
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello/{id}")
public void hello(@PathVariable Integer id,@MatrixVariable String name) {
System.out.println("id = " + id);
System.out.println("name = " + name);
}另外我们还需要配置一下 SpringMVC,使 ; 不要被自动移除了:
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Override
protected void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
}然后启动项目(注意,Spring Security 中也已经配置了允许 URL 中存在 ;),浏览器发送如下请求:
http://localhost:8080/hello/123;name=javaboy控制台打印信息如下:
id = 123
name = javaboy可以看到,@MatrixVariable 注解已经生效了。
2.3 必须是标准化 URL
请求地址必须是标准化 URL。
什么是标准化 URL?标准化 URL 主要从四个方面来判断,我们来看下源码:
StrictHttpFirewall#isNormalized:
private static boolean isNormalized(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (!isNormalized(request.getRequestURI())) {
return false;
}
if (!isNormalized(request.getContextPath())) {
return false;
}
if (!isNormalized(request.getServletPath())) {
return false;
}
if (!isNormalized(request.getPathInfo())) {
return false;
}
return true;
}getRequestURI 就是获取请求协议之外的字符;getContextPath 是获取上下文路径,相当于是 project 的名字;getServletPath 这个就是请求的 servlet 路径,getPathInfo 则是除过 contextPath 和 servletPath 之后剩余的部分。
这四种路径中,都不能包含如下字符串:
"./", "/../" or "/."2.4 必须是可打印的 ASCII 字符
如果请求地址中包含不可打印的 ASCII 字符,请求则会被拒绝,我们可以从源码中看出端倪:
StrictHttpFirewall#containsOnlyPrintableAsciiCharacters
private static boolean containsOnlyPrintableAsciiCharacters(String uri) {
int length = uri.length();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = uri.charAt(i);
if (c < '\u0020' || c > '\u007e') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}2.5 双斜杠不被允许
如果请求地址中出现双斜杠,这个请求也将被拒绝。双斜杠 // 使用 URL 地址编码之后,是 %2F%2F,其中 F 大小写无所谓,所以请求地址中也能不出现 “%2f%2f”, “%2f%2F”, “%2F%2f”, “%2F%2F”。
如果你希望请求地址中可以出现 // ,可以按照如下方式配置:
@Bean
HttpFirewall httpFirewall() {
StrictHttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
firewall.setAllowUrlEncodedDoubleSlash(true);
return firewall;
}2.6 % 不被允许
如果请求地址中出现 %,这个请求也将被拒绝。URL 编码后的 % 是 %25,所以 %25 也不能出现在 URL 地址中。
如果希望请求地址中可以出现 %,可以按照如下方式修改:
@Bean
HttpFirewall httpFirewall() {
StrictHttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
firewall.setAllowUrlEncodedPercent(true);
return firewall;
}2.7 正反斜杠不被允许
如果请求地址中包含斜杠编码后的字符 %2F 或者 %2f ,则请求将被拒绝。
如果请求地址中包含反斜杠 \ 或者反斜杠编码后的字符 %5C 或者 %5c ,则请求将被拒绝。
如果希望去掉如上两条限制,可以按照如下方式来配置:
@Bean
HttpFirewall httpFirewall() {
StrictHttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
firewall.setAllowBackSlash(true);
firewall.setAllowUrlEncodedSlash(true);
return firewall;
}2.8 . 不被允许
如果请求地址中存在 . 编码之后的字符 %2e、%2E,则请求将被拒绝。
如需支持,按照如下方式进行配置:
@Bean
HttpFirewall httpFirewall() {
StrictHttpFirewall firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
firewall.setAllowUrlEncodedPeriod(true);
return firewall;
}2.9 小结
需要强调一点,上面所说的这些限制,都是针对请求的 requestURI 进行的限制,而不是针对请求参数。例如你的请求格式是:
http://localhost:8080/hello?param=aa%2ebb
那么 2.7 小节说的限制和你没关系。
这个大家从 StrictHttpFirewall 源码中很容易看到:
public class StrictHttpFirewall implements HttpFirewall {
@Override
public FirewalledRequest getFirewalledRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws RequestRejectedException {
rejectForbiddenHttpMethod(request);
rejectedBlacklistedUrls(request);
rejectedUntrustedHosts(request);
if (!isNormalized(request)) {
throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the URL was not normalized.");
}
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();
if (!containsOnlyPrintableAsciiCharacters(requestUri)) {
throw new RequestRejectedException("The requestURI was rejected because it can only contain printable ASCII characters.");
}
return new FirewalledRequest(request) {
@Override
public void reset() {
}
};
}
private void rejectedBlacklistedUrls(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (String forbidden : this.encodedUrlBlacklist) {
if (encodedUrlContains(request, forbidden)) {
throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the URL contained a potentially malicious String \"" + forbidden + "\"");
}
}
for (String forbidden : this.decodedUrlBlacklist) {
if (decodedUrlContains(request, forbidden)) {
throw new RequestRejectedException("The request was rejected because the URL contained a potentially malicious String \"" + forbidden + "\"");
}
}
}
private static boolean encodedUrlContains(HttpServletRequest request, String value) {
if (valueContains(request.getContextPath(), value)) {
return true;
}
return valueContains(request.getRequestURI(), value);
}
private static boolean decodedUrlContains(HttpServletRequest request, String value) {
if (valueContains(request.getServletPath(), value)) {
return true;
}
if (valueContains(request.getPathInfo(), value)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static boolean valueContains(String value, String contains) {
return value != null && value.contains(contains);
}
}rejectedBlacklistedUrls 方法就是校验 URL 的,该方法逻辑很简单,我就不再赘述了。
注意:虽然我们可以手动修改 Spring Security 中的这些限制,但是不建议大家做任何修改,每一条限制都有它的原由,每放开一个限制,就会带来未知的安全风险。