阅读完需:约 13 分钟
从今天开始我们来看 Es 中常见的 23 种映射参数。
官网:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-params.html
analyzer
定义文本字段的分词器。默认对索引和查询都是有效的。
假设不用分词器,我们先来看一下索引的结果,创建一个索引并添加一个文档:
PUT blog
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"title":"定义文本字段的分词器。默认对索引和查询都是有效的。"
}查看词条向量(term vectors)
GET blog/_termvectors/1
{
"fields": ["title"]
}
查看结果如下:
{
"_index" : "blog",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"took" : 16,
"term_vectors" : {
"title" : {
"field_statistics" : {
"sum_doc_freq" : 22,
"doc_count" : 1,
"sum_ttf" : 23
},
"terms" : {
"义" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 1,
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2
}
]
},
"分" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 7,
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 8
}
]
},
"和" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 15,
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 17
}
]
},
"器" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 9,
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 10
}
]
},
"字" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 4,
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5
}
]
},
"定" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 0,
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1
}
]
},
"对" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 12,
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 14
}
]
},
"引" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 14,
"start_offset" : 15,
"end_offset" : 16
}
]
},
"效" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 21,
"start_offset" : 22,
"end_offset" : 23
}
]
},
"文" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 2,
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3
}
]
},
"是" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 19,
"start_offset" : 20,
"end_offset" : 21
}
]
},
"有" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 20,
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 22
}
]
},
"本" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 3,
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4
}
]
},
"查" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 16,
"start_offset" : 17,
"end_offset" : 18
}
]
},
"段" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 5,
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6
}
]
},
"的" : {
"term_freq" : 2,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 6,
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7
},
{
"position" : 22,
"start_offset" : 23,
"end_offset" : 24
}
]
},
"索" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 13,
"start_offset" : 14,
"end_offset" : 15
}
]
},
"认" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 11,
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 13
}
]
},
"词" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 8,
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 9
}
]
},
"询" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 17,
"start_offset" : 18,
"end_offset" : 19
}
]
},
"都" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 18,
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 20
}
]
},
"默" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 10,
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 12
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
默认情况下,中文就是一个字一个字的分,这种分词方式没有任何意义。如果这样分词,查询就只能按照一个字一个字来查,像下面这样:
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": "定"
}
}
}无意义!!!
所以,我们要根据实际情况,配置合适的分词器。
给字段设定分词器:
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
}
}
}
}存储文档:
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"title":"定义文本字段的分词器。默认对索引和查询都是有效的。"
}查看词条向量:
GET blog/_termvectors/1
{
"fields": ["title"]
}查询结果如下:
{
"_index" : "blog",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"took" : 1,
"term_vectors" : {
"title" : {
"field_statistics" : {
"sum_doc_freq" : 12,
"doc_count" : 1,
"sum_ttf" : 13
},
"terms" : {
"分词器" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 4,
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 10
}
]
},
"和" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 8,
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 17
}
]
},
"字段" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 2,
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 6
}
]
},
"定义" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 0,
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2
}
]
},
"对" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 6,
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 14
}
]
},
"文本" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 1,
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 4
}
]
},
"有效" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 11,
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 23
}
]
},
"查询" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 9,
"start_offset" : 17,
"end_offset" : 19
}
]
},
"的" : {
"term_freq" : 2,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 3,
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7
},
{
"position" : 12,
"start_offset" : 23,
"end_offset" : 24
}
]
},
"索引" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 7,
"start_offset" : 14,
"end_offset" : 16
}
]
},
"都是" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 10,
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 21
}
]
},
"默认" : {
"term_freq" : 1,
"tokens" : [
{
"position" : 5,
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 13
}
]
}
}
}
}
}然后就可以通过词去搜索了:
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": "索引"
}
}
}search_analyzer
查询时候的分词器。默认情况下,如果没有配置 search_analyzer,则查询时,首先查看有没有 search_analyzer,有的话,就用 search_analyzer 来进行分词,如果没有,则看有没有 analyzer,如果有,则用 analyzer 来进行分词,否则使用 es 默认的分词器。
normalizer
normalizer 参数用于解析前(索引或者查询)的标准化配置。
比如,在 es 中,对于一些我们不想切分的字符串,我们通常会将其设置为 keyword,搜索时候也是使用整个词进行搜索。如果在索引前没有做好数据清洗,导致大小写不一致,例如 javaboy 和 JAVABOY,此时,我们就可以使用 normalizer 在索引之前以及查询之前进行文档的标准化。
先来一个反例,创建一个名为 blog 的索引,设置 author 字段类型为 keyword:
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"author":{
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}添加两个文档:
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"author":"javaboy"
}
PUT blog/_doc/2
{
"author":"JAVABOY"
}然后进行搜索:
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"author": "JAVABOY"
}
}
}大写关键字可以搜到大写的文档,小写关键字可以搜到小写的文档。
如果使用了 normalizer,可以在索引和查询时,分别对文档进行预处理。
normalizer 定义方式如下:
PUT blog
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"normalizer":{
"my_normalizer":{
"type":"custom",
"filter":["lowercase"]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"author":{
"type": "keyword",
"normalizer":"my_normalizer"
}
}
}
}在 settings 中定义 normalizer,然后在 mappings 中引用。
测试方式和前面一致。此时查询的时候,大写关键字也可以查询到小写文档,因为无论是索引还是查询,都会将大写转为小写。
boost
boost 参数可以设置字段的权重。
boost 有两种使用思路,一种就是在定义 mappings 的时候使用,在指定字段类型时使用;另一种就是在查询时使用。
实际开发中建议使用后者,前者有问题:如果不重新索引文档,权重无法修改。
mapping 中使用 boost(不推荐):
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"content":{
"type": "text",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
}另一种方式就是在查询的时候,指定 boost
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": {
"query": "你好",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
}coerce
coerce 用来清除脏数据,默认为 true。
例如一个数字,在 JSON 中,用户可能写错了:
{"age":"99"} {"age":"99.0"}这些都不是正确的数字格式。
通过 coerce 可以解决该问题。
默认情况下,以下操作没问题,就是 coerce 起作用:(错误)
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
POST blog/_doc
{
"age":"99.0"
}如果需要修改 coerce ,方式如下:
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age":{
"type": "integer",
"coerce": false
}
}
}
}
POST blog/_doc
{
"age":99
}当 coerce 修改为 false 之后,数字就只能是数字了,不可以是字符串,该字段传入字符串会报错。
copy_to
这个属性,可以将多个字段的值,复制到同一个字段中。
定义方式如下:
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "full_content"
},
"content":{
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "full_content"
},
"full_content":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"title":"你好ElasticSearch",
"content":"当 coerce 修改为 false 之后,数字就只能是数字了,不可以是字符串,该字段传入字符串会报错。"
}
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"full_content": "当"
}
}
}doc_values 和 fielddata
es 中的搜索主要是用到倒排索引,doc_values 参数是为了加快排序、聚合操作而生的。当建立倒排索引的时候,会额外增加列式存储映射。
doc_values 默认是开启的,如果确定某个字段不需要排序或者不需要聚合,那么可以关闭 doc_values。
大部分的字段在索引时都会生成 doc_values,除了 text。text 字段在查询时会生成一个 fielddata 的数据结构,fieldata 在字段首次被聚合、排序的时候生成。
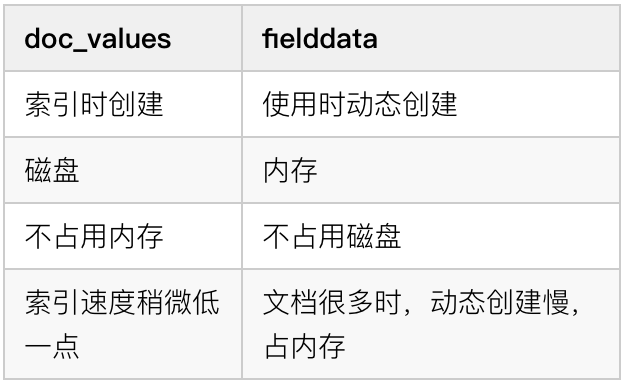
doc_values 默认开启,fielddata 默认关闭。
doc_values 演示:
PUT users
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"age":100
}
PUT users/_doc/2
{
"age":99
}
PUT users/_doc/3
{
"age":98
}
PUT users/_doc/4
{
"age":101
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort":[
{
"age":{
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}由于 doc_values 默认时开启的,所以可以直接使用该字段排序,如果想关闭 doc_values ,如下:
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age":{
"type": "integer",
"doc_values": false
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"age":100
}
PUT users/_doc/2
{
"age":99
}
PUT users/_doc/3
{
"age":98
}
PUT users/_doc/4
{
"age":101
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort":[
{
"age":{
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "Can't load fielddata on [age] because fielddata is unsupported on fields of type [integer]. Use doc values instead."
}
],
"type" : "search_phase_execution_exception",
"reason" : "all shards failed",
"phase" : "query",
"grouped" : true,
"failed_shards" : [
{
"shard" : 0,
"index" : "users",
"node" : "NV1fNVsWSIyXrUencxlRjw",
"reason" : {
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "Can't load fielddata on [age] because fielddata is unsupported on fields of type [integer]. Use doc values instead."
}
}
],
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "Can't load fielddata on [age] because fielddata is unsupported on fields of type [integer]. Use doc values instead.",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "Can't load fielddata on [age] because fielddata is unsupported on fields of type [integer]. Use doc values instead."
}
}
},
"status" : 400
}
dynamic
- 动态映射(dynamic:true)
- 静态映射(dynamic:false)
- 严格模式(dynamic:strict)
之前有过介绍
enabled
es 默认会索引所有的字段,但是有的字段可能只需要存储,不需要索引。此时可以通过 enabled 字段来控制:
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"enabled": false
}
}
}
}
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"title":"javaboy"
}
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": "javaboy"
}
}
}
返回:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
设置了 enabled 为 false 之后,就可以再通过该字段进行搜索了。
format
日期格式。format 可以规范日期格式,而且一次可以定义多个 format。
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"birthday":{
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd||yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"birthday":"2020-11-11"
}
PUT users/_doc/2
{
"birthday":"2020-11-11 11:11:11"
}- 多个日期格式之间,使用 || 符号连接,注意没有空格。
- 如果用户没有指定日期的 format,默认的日期格式是
strict_date_optional_time||epoch_mills
所有的日期格式 :
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-date-format.html
ignore_above
igbore_above 用于指定分词和索引的字符串最大长度,超过最大长度的话,该字段将不会被索引,这个字段只适用于 keyword 类型。
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 10
}
}
}
}
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"title":"javaboy"
}
PUT blog/_doc/2
{
"title":"javaboyjavaboyjavaboy"
}
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": "javaboyjavaboyjavaboy"
}
}
}
返回:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
ignore_malformed
ignore_malformed 可以忽略不规则的数据,该参数默认为 false。
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"birthday":{
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd||yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
},
"age":{
"type": "integer",
"ignore_malformed": true
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"birthday":"2020-11-11",
"age":99
}
PUT users/_doc/2
{
"birthday":"2020-11-11 11:11:11",
"age":"abc"
}
PUT users/_doc/2
{
"birthday":"2020-11-11 11:11:11aaa",
"age":"abc"
}
返回:
只有最后一个错误,因为birthday没有无视规则:
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [birthday] of type [date] in document with id '2'. Preview of field's value: '2020-11-11 11:11:11aaa'"
}
],
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [birthday] of type [date] in document with id '2'. Preview of field's value: '2020-11-11 11:11:11aaa'",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse date field [2020-11-11 11:11:11aaa] with format [yyyy-MM-dd||yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss]",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "date_time_parse_exception",
"reason" : "Failed to parse with all enclosed parsers"
}
}
},
"status" : 400
}
include_in_all
这个是针对 _all 字段的,但是在 es7 中,该字段已经被废弃了。
index
index 属性指定一个字段是否被索引,该属性为 true 表示字段被索引,false 表示字段不被索引。
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age":{
"type": "integer",
"index": false
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"age":99
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age": 99
}
}
}如果 index 为 false,则不能通过对应的字段搜索。
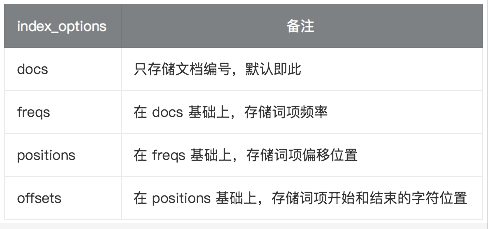
index_options
index_options 控制索引时哪些信息被存储到倒排索引中(用在 text 字段中),有四种取值:
norms
norms 对字段评分有用,text 默认开启 norms,如果不是特别需要,不要开启 norms。
null_value
在 es 中,值为 null 的字段不索引也不可以被搜索,null_value 可以让值为 null 的字段显式的可索引、可搜索:
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name":{
"type": "keyword",
"null_value": "javaboy_null"
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"name":null,
"age":99
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": "javaboy_null"
}
}
}position_increment_gap
被解析的 text 字段会将 term 的位置考虑进去,目的是为了支持近似查询和短语查询,当我们去索引一个含有多个值的 text 字段时,会在各个值之间添加一个假想的空间,将值隔开,这样就可以有效避免一些无意义的短语匹配,间隙大小通过 position_increment_gap 来控制,默认是 100。
PUT users
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"name":["zhang san","li si"]
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"name": {
"query": "sanli"
}
}
}
}sanli 搜索不到,因为两个短语之间有一个假想的空隙,为 100。
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"name": {
"query": "san li",
"slop": 101
}
}
}
}可以通过 slop 指定空隙大小。
也可以在定义索引的时候,指定空隙:
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name":{
"type": "text",
"position_increment_gap": 0
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"name":["zhang san","li si"]
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"name": {
"query": "san li"
}
}
}
}properties
映射参数
类型映射、object字段和nested字段包含子字段,称为properties,这些属性可以是任何数据类型,包括object和nested,可以添加属性:
- 在创建索引时显式地定义它们。
- 在使用
PUT mappingAPI添加或更新映射类型时显式地定义它们。 - 仅通过索引包含新字段的文档就可以动态地映射属性。
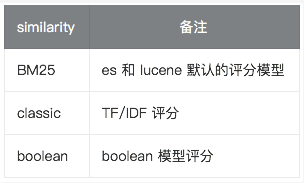
similarity
similarity 指定文档的评分模型,默认有三种:
store
默认情况下,字段会被索引,也可以搜索,但是不会存储,虽然不会被存储的,但是 _source 中有一个字段的备份。如果想将字段存储下来,可以通过配置 store 来实现。
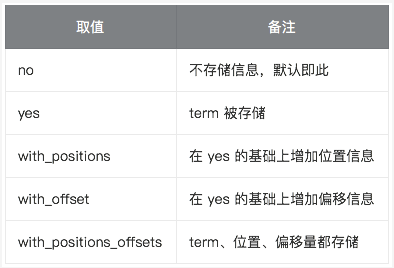
term_vectors
term_vectors 是通过分词器产生的信息,包括:
- 一组 terms
- 每个 term 的位置
- term 的首字符/尾字符与原始字符串原点的偏移量
term_vectors 取值:
fields
fields 参数可以让同一字段有多种不同的索引方式。例如:
PUT blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"raw":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"title":"javaboy"
}
GET blog/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title.raw": "javaboy"
}
}
}