阅读完需:约 8 分钟
插入式注解处理API可以让你在编译期访问注解元数据,处理和自定义你的编译输出,像反射一样访问类、字段、方法和注解等元素,创建新的源文件等等。可用于减少编写配置文件的劳动量,提高代码可读性等等。
Spring Boot 自定义注解(例子):
一、通过拦截器解析
1、自定义注解
AutoIdempotent
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoIdempotent {
}
2、编写关于注解要做的事情
幂等性机制 (这里是在Redis里操作token)即保证每条消息被发送且仅被发送一次。
RedisService
@Component
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public boolean setEx(String key, Object value, Long expireTime) {
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set(key, value);
redisTemplate.expire(key, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public boolean exists(String key) {
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
public boolean remove(String key) {
if (exists(key)) {
return redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
return false;
}
}
TokenService
@Component
public class TokenService {
@Autowired
RedisService redisService;
public String createToken() {
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
redisService.setEx(uuid, uuid, 10000L);
return uuid;
}
public boolean checkToken(HttpServletRequest req) throws IdempotentException {
String token = req.getHeader("token");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
token = req.getParameter("token");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
throw new IdempotentException("token 不存在");
}
}
if (!redisService.exists(token)) {
throw new IdempotentException("重复的操作");
}
boolean remove = redisService.remove(token);
if (!remove) {
throw new IdempotentException("重复的操作");
}
return true;
}
}
3、编写全局异常捕获
GlobalException
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalException {
@ExceptionHandler(IdempotentException.class)
public String idempotentException(IdempotentException e) {
return e.getMessage();
}
}
IdempotentException
public class IdempotentException extends Exception {
public IdempotentException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
4、拦截器编写
WebMvcConfig
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
IdempotentInterceptor idempotentInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(idempotentInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}
IdempotentInterceptor
@Component
public class IdempotentInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
TokenService tokenService;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if (!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)) {
return true;
}
Method method = ((HandlerMethod) handler).getMethod();
AutoIdempotent autoIdempotent = method.getAnnotation(AutoIdempotent.class);
if (autoIdempotent != null) {
try {
return tokenService.checkToken(request);
} catch (IdempotentException e) {
throw e;
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
5、controller接口编写
HelloController
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
TokenService tokenService;
@GetMapping("/gettoken")
public String getToken() {
return tokenService.createToken();
}
@PostMapping("/hello")
@AutoIdempotent
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
@PostMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2() {
return "hello2";
}
}
二、通过 AOP 解析
1、自定义注解
AutoIdempotent
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoIdempotent {
}
2、业务编写
RedisService
@Component
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public boolean setEx(String key, Object value, Long expireTime) {
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set(key, value);
redisTemplate.expire(key, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public boolean exists(String key) {
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
public boolean remove(String key) {
if (exists(key)) {
return redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
return false;
}
}TokenService
@Component
public class TokenService {
@Autowired
RedisService redisService;
public String createToken() {
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
redisService.setEx(uuid, uuid, 10000L);
return uuid;
}
public boolean checkToken(HttpServletRequest req) throws IdempotentException {
String token = req.getHeader("token");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
token = req.getParameter("token");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
throw new IdempotentException("token 不存在");
}
}
if (!redisService.exists(token)) {
throw new IdempotentException("重复的操作");
}
boolean remove = redisService.remove(token);
if (!remove) {
throw new IdempotentException("重复的操作");
}
return true;
}
}
3、全局异常拦截
GlobalException
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalException {
@ExceptionHandler(IdempotentException.class)
public String idempotentException(IdempotentException e) {
return e.getMessage();
}
}
IdempotentException
public class IdempotentException extends Exception {
public IdempotentException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
4、AOP切面拦截
IdempotentAspect
@Component
@Aspect
public class IdempotentAspect {
@Autowired
TokenService tokenService;
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.javaboy.idempotent.annotation.AutoIdempotent)")
public void pointcut() {
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws IdempotentException {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
try {
tokenService.checkToken(request);
} catch (IdempotentException e) {
throw e;
}
}
}
5、Controller接口编写
HelloController
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
TokenService tokenService;
@GetMapping("/gettoken")
public String getToken() {
return tokenService.createToken();
}
@PostMapping("/hello")
@AutoIdempotent
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
@PostMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2() {
return "hello2";
}
}
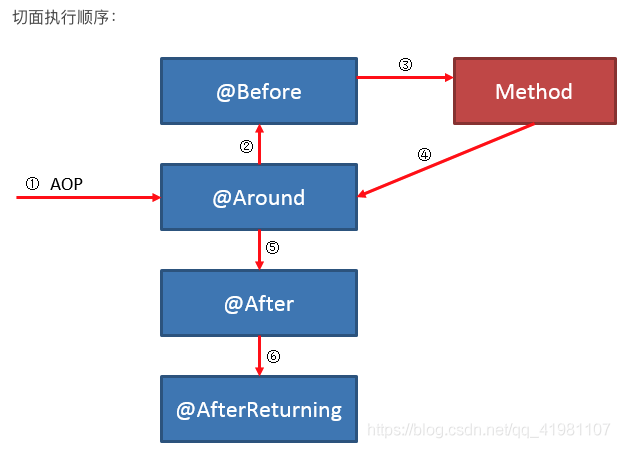
@Around简单使用示例——SpringAOP增强处理
@Around的作用
- 既可以在目标方法之前织入增强动作,也可以在执行目标方法之后织入增强动作;
- 可以决定目标方法在什么时候执行,如何执行,甚至可以完全阻止目标目标方法的执行;
- 可以改变执行目标方法的参数值,也可以改变执行目标方法之后的返回值; 当需要改变目标方法的返回值时,只能使用Around方法;
- 虽然Around功能强大,但通常需要在线程安全的环境下使用。因此,如果使用普通的Before、AfterReturing增强方法就可以解决的事情,就没有必要使用Around增强处理了。
注解方式:如果需要对某一方法进行增强,只需要在相应的方法上添加上自定义注解即可
import com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect //标注增强处理类(切面类)
@Component //交由Spring容器管理
public class AnnotationAspect {
/*
可自定义切点位置,针对不同切点,方法上的@Around()可以这样写ex:@Around(value = "methodPointcut() && args(..)")
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation)")
public void methodPointcut(){}
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation2)")
public void methodPointcut2(){}
*/
//定义增强,pointcut连接点使用@annotation(xxx)进行定义
@Around(value = "@annotation(around)") //around 与 下面参数名around对应
public void processAuthority(ProceedingJoinPoint point,MyAnnotation around) throws Throwable{
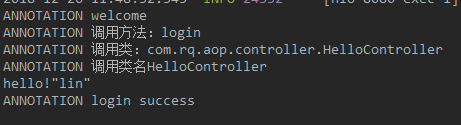
System.out.println("ANNOTATION welcome");
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用方法:"+ around.methodName());
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类:" + point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类名" + point.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());
point.proceed(); //调用目标方法
System.out.println("ANNOTATION login success");
}
}注解类
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时有效
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//作用于方法
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String methodName () default "";
}Controller
import com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/login/{name}")
@MyAnnotation(methodName = "login")
public void login(@PathVariable String name){
System.out.println("hello!"+name);
}
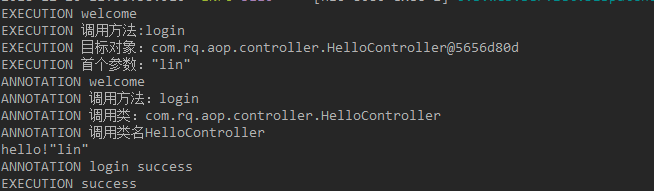
}运行结果
匹配方法执行连接点方式
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(0) //设置优先级,值越低优先级越高
public class ExecutionAspect {
@Around(value = "execution(* com.rq.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
public void processAuthority (ProceedingJoinPoint point)throws Throwable{
System.out.println("EXECUTION welcome");
System.out.println("EXECUTION 调用方法:" + point.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("EXECUTION 目标对象:" + point.getTarget());
System.out.println("EXECUTION 首个参数:" + point.getArgs()[0]);
point.proceed();
System.out.println("EXECUTION success");
}
}- 任意公共方法的执行:execution(public * (..))
- 任何一个以“set”开始的方法的执行:execution( set(..))
- AccountService 接口的任意方法的执行:execution(com.xyz.service.AccountService.(..))
- 定义在service包里的任意方法的执行: execution( com.xyz.service..(..))
- 定义在service包和所有子包里的任意类的任意方法的执行:execution(* com.xyz.service...(..))
第一个表示匹配任意的方法返回值, …(两个点)表示零个或多个,第一个…表示service包及其子包,第二个表示所有类, 第三个*表示所有方法,第二个…表示方法的任意参数个数
- 定义在pointcutexp包和所有子包里的JoinPointObjP2类的任意方法的执行:execution(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp..JoinPointObjP2.(..))”)
- pointcutexp包里的任意类: within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.) pointcutexp包和所有子包里的任意类:within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp..)
- 实现了Intf接口的所有类,如果Intf不是接口,限定Intf单个类:this(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.Intf)
- 当一个实现了接口的类被AOP的时候,用getBean方法必须cast为接口类型,不能为该类的类型
- 带有@Transactional标注的所有类的任意方法: @within(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) @target(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- 带有@Transactional标注的任意方法:@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) @within和@target针对类的注解,@annotation是针对方法的注解
- 参数带有@Transactional标注的方法:@args(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- 参数为String类型(运行是决定)的方法: args(String)
运行结果